Creating Policies with Internet Services Database
This article describes using the Internet Services Database on a FortiGate firewall. The Internet Services Database is a comprehensive public IP address database that combines IP address range, IP owner, service port number and IP security credibility. The data comes from the FortiGuard service system and is regularly updated by Fortinet.
This database can be used as either source or destination for policies.
A few prerequisites, you have to have a valid FortiGuard subscription and the service Domain & IP Reputation needs to be enabled in System–>Feature Visibility.
Using predefined Internet Service Database elements in a policy.
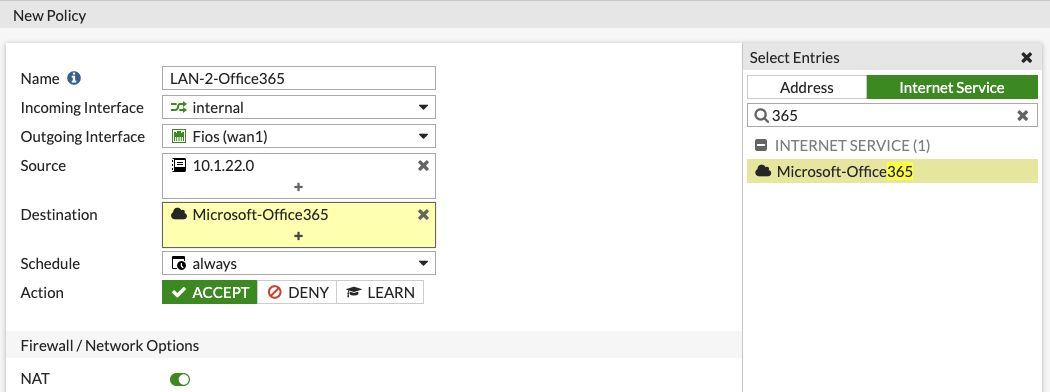
This example will create a policy allowing traffic to the Microsoft Office 365 Internet Service from the LAN.
- Navigate to Policy & Objects –> IPv4 Policy
- Click Create New
- Name: Descriptive Policy Name
- Incoming interface: internal
- Outgoing interface: WAN1
- Source: select your LAN source address object
- Destination: Click Internet Service and select Microsoft-Office365
- The rest of the settings should follow your standard rules creation process
Diagnosing Internet Service Policy Database Elements
Each Internet Service has a unique ID. If you navigate to Policy & Objects –>Internet Services Database you can mouse over the entry you want to diagnose and it will show the service ID.
This example will diagnose the Microsoft Office 365 object, it has an object ID of 327782.
From the CLI:
diag internet-service id-summary 327782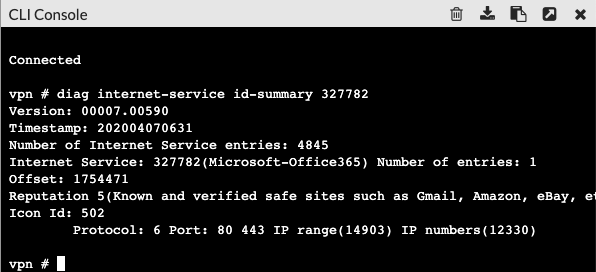
Custom Internet Service Policy
Even though there are thousands of predefined Internet Services, sometimes you need to create your own Internet Service entry.
When you create a custom Internet Service you need to set the following elements:
- IP or IP ranges
- Protocol number
- Port or Port ranges
- Reputation
You also need to do this from the CLI, the syntax is:
config firewall internet-service-custom
edit <name>
set comment <comment>
set reputation {1|2|3|4|5}
config entry edit <ID#>
set protocol <number #>
set dst <object_name>
config port-range
edit <ID#>
set start-port <number #>
set end-port <number #>
next
end
next
end
end